How Many O2 Sensors Does a Car Have? (Every Types Explained)
O2 sensors are vital for emission control and fuel efficiency, along with your car’s overall performance. Different types of O2 sensors perform unique tasks along with their intended use. So, it’s normal that you would want to know how many O2 sensors does a car have?
Well, it depends on the car model and manufacturer. Some have only two, while others have four and sometimes even more O2 sensors. The number of O2 sensors depends on the following:
- The engine type
- Manufacturer
- Car Model
What Are Car O2 Sensors?

O2 sensors, or lambda sensors, are crucial components of a car’s engine management system. Theymainly monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases emitted by the engine and provide real-time feedback to the engine control unit or ECU.
How Many O2 Sensors Does a Car Have?
The number of oxygen sensors in a car will vary depending on the manufacturer, model, year of creation and engine type. These days,cars typically have two to four oxygen sensors in them.
Oxygen Sensor Count Based on Engine
- Four-Cylinder Engine
A four-cylinder engine is the most common among modern vehicles, and it comes with two oxygen sensors.
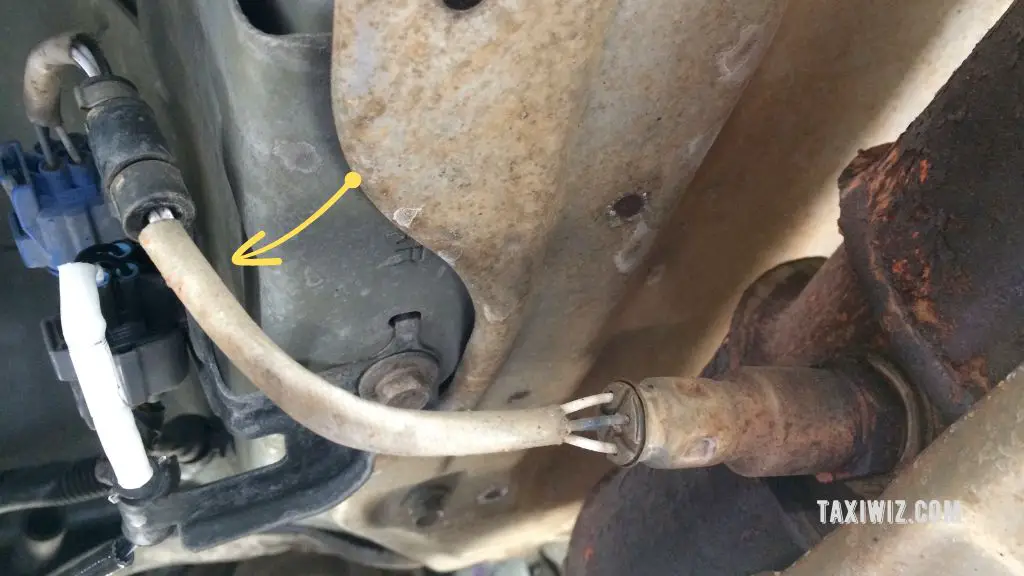
The first one is located right before the catalytic converter and often is referred to as the “upstream” sensor. The second one is placed after the catalytic converter and labeled the “downstream” sensor.
- Six or Eight-Cylinder Engine
Cars with six or eight-cylinder engines come with four oxygen sensors, two of which are upstream sensors located at each bank of cylinders. The remaining two are downstream sensors located after the catalytic converter.
Oxygen Sensor Count Based on Advanced Emission Control Systems.
Apart from the engine type, some modern cars come with advanced emission control systems.
In these cars, the O2 sensor count can be over four as these sensors can monitor specific areas of the exhaust system to generate more specific data for engine management and emissions control.
Types of O2 Sensors
Different types of O2 sensors are used in vehicles, and each offers a different approach to measuring the oxygen content in exhaust gases. The most well-known ones are the following:
1. Zirconia Sensors
Narrowband, or Zirconia sensors, are cars’ most common O2 sensors. They are made of a ceramic element consistingof zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) and platinum electrodes on either side. Theyare typically used for controlling the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio.
These sensors operate following the principle of an oxygen concentration cell which measures the difference in oxygen levels from the exhaust air and the air outsidethe sensor.
It then creates a voltage signal that is sent to the ECU, and the system then adjusts the air-fuel mixture. These sensors are highly accurate within a narrow stoichiometric range.
2. Wideband or AFR Sensors
Wideband, mostly known as Air Fuel Ratio (AFR) sensors, are upgraded versions of Zirconia sensors. They can detect rich or excess fuel and lean or insufficient fuel situations.
These sensors can measure the exact air-fuel ratio and provide a precise output voltage signal for the ECU. In advanced engine management systems, these sensors shine the most.
3. Dual Cell Sensors
Titania or Dual Cell sensors use titanium dioxide (TiO2) as their primary sensing material. These sensors consist of two chambers separated by the titania element; one of them is exposed to the exhaust gas while the other is to ambient air.
The difference in oxygen between the two chambers generates a voltage signal which is sent to the ECU.
They also cost significantly less than the Zirconia or AFR sensors, but on the contrary, they are less accurate. We can find these sensors in older car models mostly.
4. Electrochemical Sensors
As the name suggests, electrochemical sensors usea chemical reaction between oxygen and an electrode to provide data for the ECU. They come with an electrolyte and two electrodes.
The oxygen molecules diffuse and react at the sensing electrode,generating an electrical current that measures the exhaust gas oxygen amount.
Nowadays, electrochemical sensors are quite rare in vehicles as the other options are far superior and require fewer chemical components to work.
Why Are O2 Sensors Significant?

You maybe wondering why O2 sensors areimportant for a car. These are the reasons why:
Monitoring Exhaust Gas Composition
O2 sensors are primarily responsible for monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. They will provide real-time feedback on the oxygen levels present in the exhaust stream.
This information helps the ECU to make necessary adjustments to the fuel injection system to maintain the most optimal air-fuel ratio.
Optimization Air-Fuel Mixture
From the data gainedO2 sensors, the ECU adjusts the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chambers to the stoichiometric ratio, which varies depending on the fuel type. The stoichiometric ratio is referred to as the perfect air-fuel ratio for cars.
Achieving Efficient Combustion
By maintaining the optimal stoichiometric ratio, O2 sensors help to get efficient combustion for the engine, which ensures that fuel is burned completely and maximum power output is available through minimal fuel wastage. It also offers better fuel economy, improved engine performance, and reduced emissions.
Emission Control
O2 sensors reduce the chance of harmful emissions. They ensure the proper functioning of the catalytic converter, which relies on the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. This ensures a lower number of pollutants are exhausted in the air.
Real-Time Feedback Loop
These sensors work as a continuous feedback loop for the engine and the ECU. This loop enables the engine to adapt and evolve to changing situations and life differences in load, temperature, fuel quality, and altitude.
Diagnostics and Fault Detection:
O2 sensors work as diagnostic tools as well. They can notify about potential issues within the engine system and can trigger the “Check Engine” light on the car’s dashboard. This way, the driver can easily spot an engine issue before it becomes severe.
Can You Add Extra O2 Sensors to Your Car?
Yes, you can add extra O2 sensors in most modern car models, but a few factors need to be checked before making any firm decision.
Adding O2 sensors to a car is a complex task that requires technical understanding, proper experience, and access to quality tools and equipment. Unless you possess these qualities, we recommend you consult with a professional mechanic before you go ahead and try to add O2 sensors to your car.
Here are some factors that you will have to bear in mind when considering adding extra O2 sensors in your car:
Engine Compatibility
O2 sensors are generally integrated into your car’s engine’s exhaust system when they are in the manufacturing process.
So, adding extra O2 sensors to an engine means that you will have to modify the exhaust system. The modifications will vary from one engine model to another.
Therefore, you will need to have proper knowledge of car engines and their exhaust system to install them, and the engine must have the option to add a few O2 sensors in the exhaust system.
In older engine models, this option isn’t available. So, it becomes a compatibility issue when installing additional O2 sensors in them.
ECU Compatibility
Much like the engine ECU in your car should be capable of enlisting and processing the signals from the extra O2 sensors you are planning to install.
Some ECUs don’t have the necessary inputs or software upgrades that can handle the data from extra sensors. In these scenarios, you will have to either install a new ECU or completely reprogram the ECU so that it can read the data from the new sensors. You may have to install a new processing chip on your ECU for this.
Wiring and Connections
If the engine and ECU is compatible, you must worry about the wiring. Putting extra O2 sensors in a car requires a complete overhaul of the wiring system along with the connectors.
A few things you will have to remember regarding the wiring is that the sensors must be connected to the ECU; for this, wiring harnesses might have to be installedto ensure accurate data transmission.
You will also have to consider the protection of the writing. Keeping it safe from heat, moisture, and vibration isn’t easy. Protective wires and sealant will also come into play in this case.
Sensor Calibration
Once you have finally installed the additional O2 sensors, you need to ensure that they are functioning properly. For that, you will need to get them calibrated and synchronized with the ECU.
Otherwise, the ECU won’t be able to accurately interpret the signals from the sensors,nor can it adjust the air-fuel mixture according to the right ratio.
You will have to use special equipment for the calibration and synchronization part.
Modification Rules and Ethics
Lastly, you will also need to consider the local transport laws and regulations regarding modifications and emissions.
If you don’t abide by the rules, then your modified car will be regarded as an offense, and you will be penalized. What’s more, you won’t be able to put your car on the road if it breaks the rules for safe conduct, modification, and emission.
So, all that trouble you went through for the modification will be for nothing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of O2 sensors?
To monitor oxygen levels on exhaust gases to figure out efficient combustion, fuel efficiency and emission control.
2. How long do O2 sensors last?
The general lifespan of O2 sensors is fifty thousand to one hundred thousand miles.
3. Do damaged O2 sensors affect fuel economy?
Yes, it provides inaccurate readings, which can result in a steady decrease in fuel efficiency.
Final Thoughts
O2 sensors allow a car to function optimally and ensure proper combustion and exhaust. Therefore, understanding how many O2 sensors a car have will give you a better insight into the functionality of a vehicle.
While the higher quantity is often the best option, do consider the car model and engine before you judge a vehicle just by its O2 sensors.